Natural Language Query in OpenCTI: Leveraging AI to target specific entities
In the fast-paced world of cybersecurity, the ability to navigate massive datasets quickly & effectively has become critical to elevating your security posture. These datasets often comprise numerous inter-connected entities that can create a massive & complex set of filtering possibilities. With the introduction of Natural Language Query (NLQ), OpenCTI 6.6 empowers analysts to interact with threat intelligence using natural language. Simply ask questions or assertions in your native language and receive structured, actionable results in the form of a filtered OpenCTI entities list. No more complex filters syntaxes – OpenCTI will generate them for you!
Let’s explore how NLQ works in OpenCTI, how it can enhance productivity for analysts and make working with cyber threat intelligence more intuitive than ever!
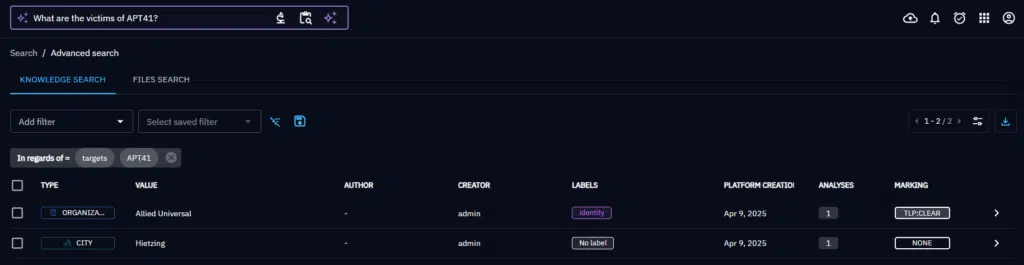
Searching with NLQ
Easily click on the ‘Ask AI’ button in the OpenCTI search bar to activate NLQ mode and type your question. Ask AI will generate filters and determine the entities corresponding to your request.

The AI Large Language Model (LLM)
Ask AI uses our Large Language Model (LLM) to generate filters based on your question. The prompt contains:
- the user input assertion
- examples of questions associated with their expected outcome
- the OpenCTI filters format
- additional constraints for the result
Other Considerations
The filter keys should exist in OpenCTI (attributes, relations input names and some special filter keys):,
- the operators should be among the ones supported (’equals’, ‘greater than’, ‘contains’, etc.),
- for filter keys whose values are entity types, the model can only put existing entity and relationship types in the filter values.
NLQ filters the result to display the list of matching entities.
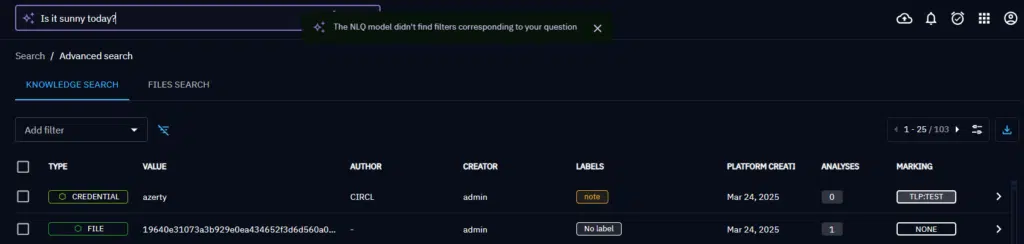
If the question is not understood or out of the OpenCTI cyber context, no filters may be found.
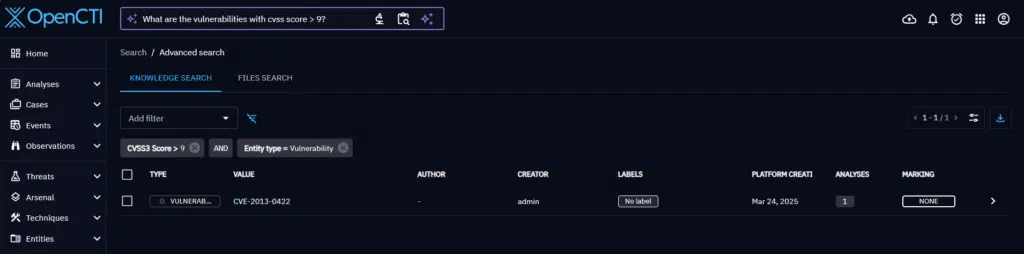
Entity ID mapping in the platform
When a question includes a term corresponding to a platform entity, the generated filters should reference the ID of that entity. Thus the generated filters should be post-processed to turn such terms into IDs.
The NLQ filters results is composed of a list of filters with a key, operator, mode, and some values. For the filters whose key represents entities, the provided values are extracted. A search is then performed among the platform data across multiple fields (name, value, aliases, etc.) to find entities matching each values.
If matches are found, the best match ID will be used in the generated filters.
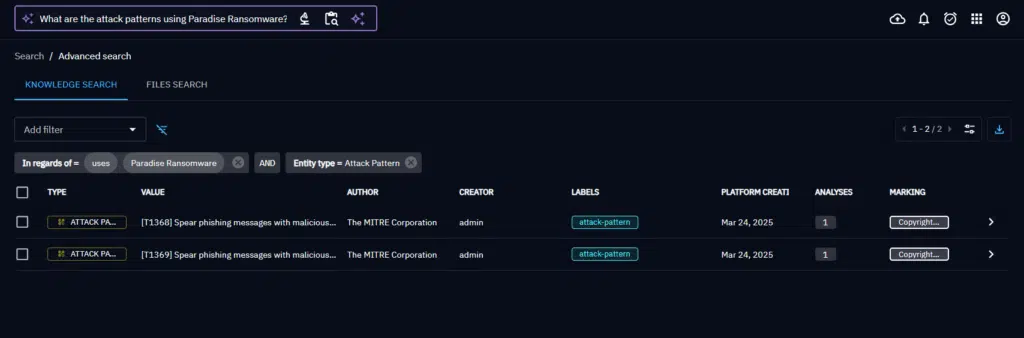
If no match is found, the part of the filters involving the entity will be skipped.
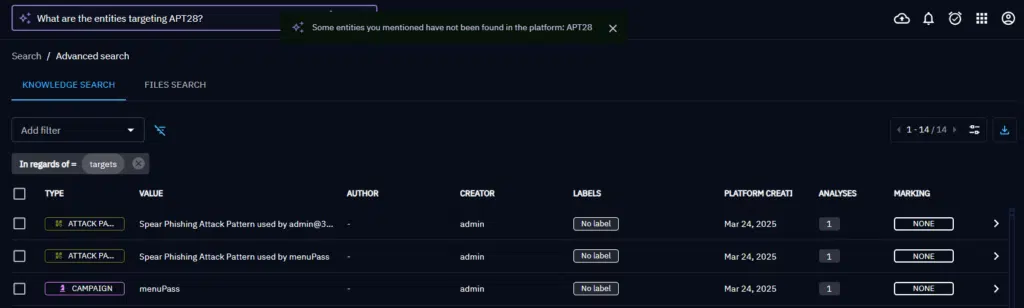
Current NLQ model limitations
As NLQ was recently introduced in OpenCTI, additional development work is still underway. Additional features and the ability to handle all use cases will be introduced in future versions.
OpenCTI 6.6 for example does not yet provide the ability to search among relationships (only entities), dates may not be fully understood and the model cannot filter on related entities properties (second level information). We are working on an LLM model that returns filters with multi-level logic combinations (e.g., mixing AND/OR modes between different filters). Therefore filters are currently limited to one level of imbrication: a list of filters separated by a single and/or mode.
Token usage and costs notice
The Natural Language Query feature relies on heavy prompts sent to the language model to describe the filters structure and provide examples. These complex queries may generate significant token usage. When using a custom API endpoint (e.g., OpenAI, Mistral, AzureAI) with your own API key, this may result in increased costs.
For existing Filigran SaaS Enterprise customers, queries are routed through our hosted model instance and do not incur additional costs.
Conclusion
OpenCTI’s NLQ is a major step toward making threat intelligence more accessible & intuitive. Now users can interact with data using native language. NLQ facilitates the development of complex searches that used to require deep platform knowledge. With NLQ, security teams can respond faster and more effectively by turning questions into insights! As the feature evolves, NLQ can “up-level” your Security teams, further reducing the gap between human intent and CTI desired results, making OpenCTI a the choice for threat intelligence teams around the globe.
If you have any question, request, comment or feedback to share with us, don’t hesitate to join us on Slack! 📢!
Note: OpenCTI AI features are available in the Enterprise Edition.
Read more
Explore related topics and insights
